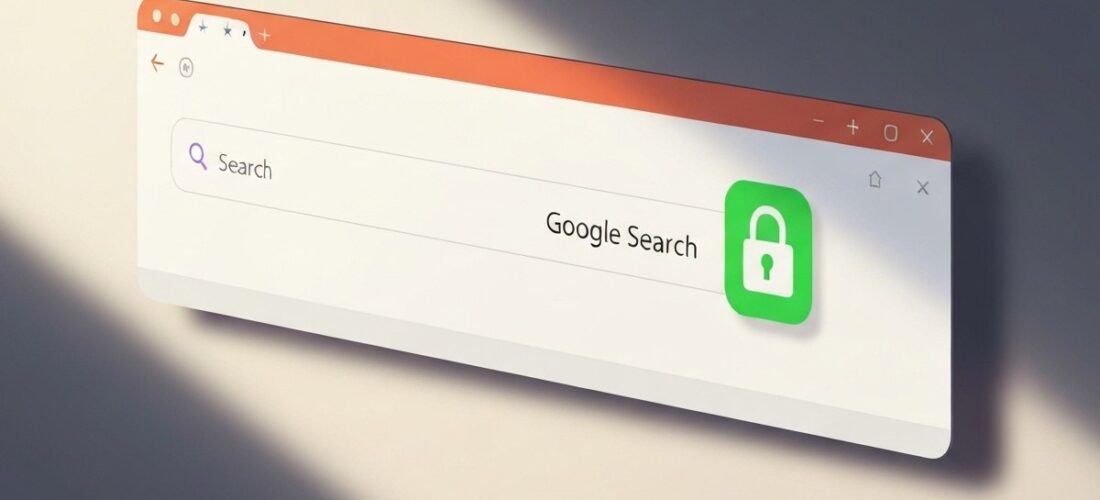
gws_rd=ssl – If you’ve ever glanced at your browser’s address bar while using Google, you might have noticed a long string of letters and symbols after google.com. One common part you may see is gws_rd=ssl. It looks technical, but understanding it reveals a simple, smart piece of how the web works to keep you safe.
What Does “gws_rd=ssl” Mean?
Let’s break down this code piece by piece to demystify it completely.
-
gws: Stands for “Google Web Server.” This is simply the name of the internal system that handles your search request. -
rd: Stands for “redirect.” This is the key action. -
ssl: Stands for “Secure Sockets Layer,” the technology that creates an encrypted, secure connection between your browser and a website. You now see it more commonly as HTTPS (with the ‘S’ standing for ‘Secure’).
Put simply, gws_rd=ssl means the Google Web Server is ensuring your connection is securely redirected to an encrypted (HTTPS) version of its service.
The “Why”: It’s All About Security (And Speed)
This parameter isn’t just random; it serves two core purposes that benefit you directly:
-
To Enforce a Secure Connection (Primary Purpose): Years ago, Google made a landmark decision to default all searches to the secure HTTPS protocol. The
rd=sslparameter is a legacy piece of this system that helps guarantee you are always using the encrypted version of Google Search (https://www.google.com/), not the old, unsecuredhttp://version. This encryption protects your search queries from being intercepted and read by others on public Wi-Fi networks, for example. -
To Handle Regional Redirects Efficiently (Secondary Purpose): The redirect mechanism (
rd) is also part of how Google seamlessly sends you to your local domain (likegoogle.co.uk,google.de, orgoogle.com.au) based on your location, while still maintaining that securesslconnection.
In short, seeing gws_rd=ssl is a good sign. It’s a behind-the-scenes confirmation that Google is actively managing your connection for optimal security and correct regional service.
Frequently Asked Questions
Should I be concerned if I see gws_rd=ssl in my URL?
No. This is a normal, benign parameter used by Google. You do not need to remove it or take any action. Its presence is routine.
Is this parameter tracking me or my searches?
No, gws_rd=ssl itself is not a tracking parameter. Its function is purely technical (security and redirection). Google uses other methods (like cookies and logged-in accounts) for personalization and history. This particular string does not identify you or your search history.
Can I manually remove it from the URL?
You can try deleting everything from the question mark (?) onward in the address bar and pressing Enter. However, Google’s systems will almost certainly re-add it (or similar parameters) to ensure you are redirected to the secure, correct version of the site. Its presence is standard.
I see other parameters like ei=, ved=, or sourceid=. What are those?
Google uses many URL parameters for various internal functions. For instance:
-
ei=often contains an encoded timestamp of when you initiated the search. -
ved=is a “viewport ID” used for analytics to understand how you interacted with the search results page (e.g., which link you clicked). -
sourceid=might identify the source of the search request (like the Chrome browser).
Unlike gws_rd=ssl, some of these can be related to analytics and measuring user interaction, but they are typically anonymized and not tied to your personal identity unless you are logged into a Google account.
Key Takeaway
The gws_rd=ssl parameter is a harmless, technical artifact of Google’s infrastructure. It exists to silently and automatically enforce a secure, encrypted connection for every one of your searches, protecting your privacy. You can safely ignore it and carry on searching, knowing it’s a small part of what keeps your web browsing more secure.